What’s the Potential for Intelligent automation in the Healthcare Payer Space?
Businesses across every sector are facing unprecedented challenges, and healthcare payers are no exception. The challenges are twofold: payers are expected to take care of subscribers during these troubled times, while also dealing with pressure to meet revenue metrics and sustain margins.
COVID-19 is a formidable adversary. The healthcare industry (as well as technology) has responded well, adapting to unexpected obstacles with innovative ways of delivering health services, including– telehealth and telemedicine. Yet, these new services bring new challenges: massive changes to the way these services are delivered and accounted for.
Additionally, new healthcare services (and delivery of them) has created a new dynamic in the payer industry. Increased operations load must be managed virtually – anytime anywhere. Managers are now expected to have end-to-end visibility, while keeping staff morale high.
Payers must be agile and ready to scale rapidly. The only way payers can deal with this challenge is to automate as much as possible, in order to provide value to subscribers and providers - all while reducing cost and keeping the employee morale high.
What is the automation potential in Healthcare Payer space?
Following a deep dive assessment with payers, Lateetud identified the following areas ripe for automation. The potential for using Intelligent Automation technologies is identified in the below table.
Focus Area: Capability-Function mapping with Technology
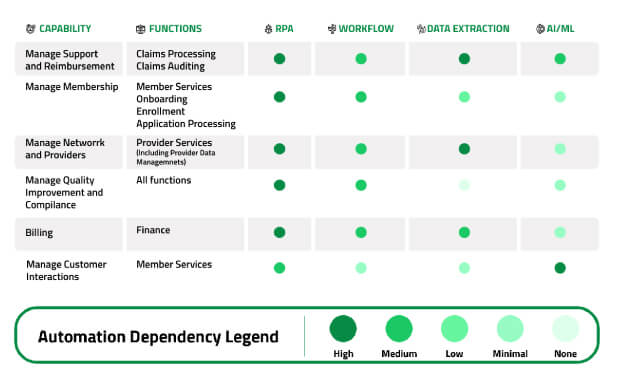
The Top Four Areas Ripe For Automation include:
Claims Processing
and Review
This is an area that has the most cost associated in payer operations. A few areas that are still manual (according to our studies) are:
- Claim Service Inventories,
- Complex or Unique Claims,
- Pre-Authorizations or Pre-Treatments,
- Member Submitted Claims,
- Medical Records or Attachments review,
- Other Routine or admin functions.
There is a big scope for data extraction from statutory forms and medical records.
Membership
Management
This area includes member onboarding, enrollment, and application processing. There are a lot of standard processes that are part of these functions that can be templatized and as a result, automated. For instance
- Transfer Accumulations
- Rekey and/or Adjustments for Onboarding
- Automated Letters and Emails
- Pre−Authorization
- Pre−Estimates
Customer
Interactions
Member Services function includes call center and customer support functions. The channel of support could include voice, SMS and email. Intelligent Automation includes several technologies, including
- Chatbots powered with Natural Language Processing
- Cognitive Contact Center Solutions
- Email Management
- Customer Portal
- Self Service
- Provider Data Confirmation
Audit and
Compliance
We are seeing the increasing potential in audit function. Audit programs in Payers assess operational and service performance by monitoring claims processing, customer service and the enrollment processing functions. Major areas for automation within Audit include
- Enrollment
- Claim
- Self service
- Manual enquiries
- First Call Resolution
References
Case Study
Leading insurance provider increases productivity by 4X and more by implementing Intelligent Automation in the Accounts Payable department.
Webinar
In less than one hour of on−demand session learn how to get started with Robotic Process Automation and how to assess processes for automation.
White Paper
In this white paper Michael Marchuk, VP Strategic Advisory Blueprism and Pawan Jadhav, CEO Lateetud discuss the challenges and opportunities faced by Healthcare Payers in COVID−19 and beyond.
The Top Four Areas Ripe For Automation include:
Claims Processing
and Review
This is an area that has the most cost associated in payer operations. A few areas that are still manual (according to our studies) are:
- Claim Service Inventories,
- Complex or Unique Claims,
- Pre-Authorizations or Pre-Treatments,
- Member Submitted Claims,
- Medical Records or Attachments review,
- Other Routine or admin functions.
There is a big scope for data extraction from statutory forms and medical records.
Membership
Management
This area includes member onboarding, enrollment, and application processing. There are a lot of standard processes that are part of these functions that can be templatized and as a result, automated. For instance
- Transfer Accumulations
- Rekey and/or Adjustments for Onboarding
- Automated Letters and Emails
- Pre−Authorization
- Pre−Estimates
Customer
Interactions
Member Services function includes call center and customer support functions. The channel of support could include voice, SMS and email. Intelligent Automation includes several technologies, including
- Chatbots powered with Natural Language Processing
- Cognitive Contact Center Solutions
- Email Management
- Customer Portal
- Self Service
- Provider Data Confirmation
Audit and
Compliance
We are seeing the increasing potential in audit function. Audit programs in Payers assess operational and service performance by monitoring claims processing, customer service and the enrollment processing functions. Major areas for automation within Audit include
- Enrollment
- Claim
- Self service
- Manual enquiries
- First Call Resolution
References
Case Study
Leading insurance provider increases productivity by 4X and more by implementing Intelligent Automation in the Accounts Payable department.
Webinar
In less than one hour of on−demand session learn how to get started with Robotic Process Automation and how to assess processes for automation.
White Paper
In this white paper Michael Marchuk, VP Strategic Advisory Blueprism and Pawan Jadhav, CEO Lateetud discuss the challenges and opportunities faced by Healthcare Payers in COVID−19 and beyond.







